|
|  |
| back to top | |
|
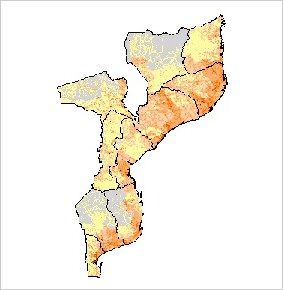
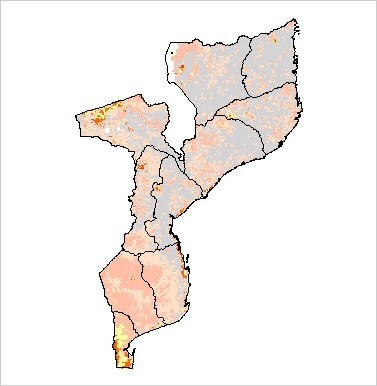
Population. Historically cheetah were relatively widespread in Mozambique with records from the north, west and southern parts of the country. More recently significant populations were only known to exist in the north west corner of Tete Province, and within and on the periphery of the Limpopo Valley and Bauhine National Parks. Previous assessment of the population concluded that the reduction of cheetah range across the country was due to hunting for skins, and a decrease in prey populations. The population of cheetahs appears to have further declined since this assessment, and recent records are reported only from the north west of Tete Province (Purchase 2007). However, given the historical distribution of cheetahs and the potential for the threats of poaching and reduction in prey to be alleviated there are areas where natural recolonisation may occur. |
|
| back to top | |
|
Almost five centuries as a Portuguese colony came to a close with independence in 1975. Large-scale emigration by whites, economic dependence on South Africa, a severe drought, and a prolonged civil war hindered the country's development. The ruling Front for the Liberation of Mozambique (FRELIMO) party formally abandoned Marxism in 1989, and a new constitution the following year provided for multiparty elections and a free market economy. A UN-negotiated peace agreement between FRELIMO and rebel Mozambique National Resistance (RENAMO) forces ended the fighting in 1992. In December 2004, Mozambique underwent a delicate transition as Joaquim CHISSANO stepped down after 18 years in office. His newly elected successor, Armando Emilio GUEBUZA, has promised to continue the sound economic policies that have encouraged foreign investment. | |
| back to top | |
|
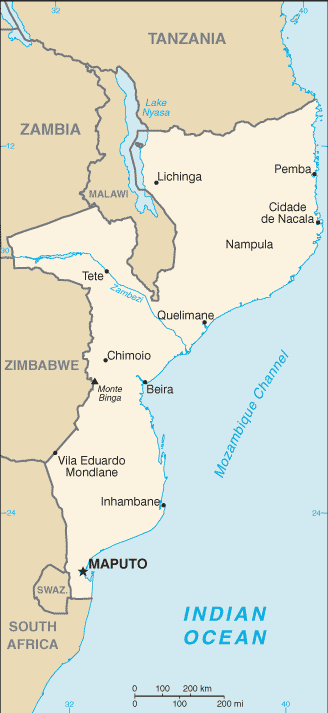
Area: total: 801,590 sq km; land: 784,090 sq km; water: 17,500 sq km Climate: tropical to subtropical Terrain: mostly coastal lowlands, uplands in center, high plateaus in northwest, mountains in west Land use: arable land: 5.43%; permanent crops: 0.29%; other: 94.28% (2005) Natural resources: coal, titanium, natural gas, hydropower, tantalum, graphite Natural hazards: severe droughts; devastating cyclones and floods in central and southern provinces Environment-current issues: a long civil war and recurrent drought in the hinterlands have resulted in increased migration of the population to urban and coastal areas with adverse environmental consequences; desertification; pollution of surface and coastal waters Environment-international agreements:
party to: Biodiversity, Climate
Change, Desertification, Endangered Species, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea,
Ozone Layer Protection
|
|
|
|
|
| back to top | |
|
Population: 19,686,505 (2006 est.) Age structure: 0-14 years: 42.7% (male 4,229,802/female 4,177,235); 15-64 years: 54.5% (male 5,207,149/female 5,519,291); 65 years and over: 2.8% (male 230,616/female 322,412) (2006 est.) Median age: total: 18.3 years; male: 17.8 years; female: 18.8 years (2006 est.) Population growth rate: 1.38% (2006 est.) Infant mortality rate: total: 129.24 deaths/1,000 live births; male: 134.31 deaths/1,000 live births; female: 124.02 deaths/1,000 live births (2006 est.) Life expectancy at birth: total population: 39.82 years; male: 39.53 years; female: 40.13 years (2006 est.) Total fertility rate: 4.82 children born/woman (2006 est.) HIV/AIDS - adult prevalence rate: 12.2% (2003 est.) HIV/AIDS - people living with HIV/AIDS: 1.3 million (2003 est.) HIV/AIDS - deaths: 110,000 (2003 est.) |
|
|
Major infectious diseases: ffood or waterborne diseases: bacterial and protozoal diarrhea, hepatitis A, and typhoid fever; vectorborne diseases: malaria and plague are high risks in some locations; water contact disease: schistosomiasis (2007) Ethnic groups: African 99.66% (Makhuwa, Tsonga, Lomwe, Sena, and others), Europeans 0.06%, Euro-Africans 0.2%, Indians 0.08% Religions: Catholic 23.8%, Muslim 17.8%, Zionist Christian 17.5%, other 17.8%, none 23.1% (1997 census) Languages: Emakhuwa 26.1%, Xichangana 11.3%, Portuguese 8.8% (official; spoken by 27% of population as a second language), Elomwe 7.6%, Cisena 6.8%, Echuwabo 5.8%, other Mozambican languages 32%, other foreign languages 0.3%, unspecified 1.3% (1997 census) Literacy: definition: age 15 and over can read and write; total population: 47.8%; male: 63.5% ; female: 32.7% (2003 est.) |
|
| back to top | |
|
Data code: MZ Government type: republic Independence: 25 June 1975 (from Portugal) Legal system: based on
Portuguese civil law system and customary law | |
| back to top | |
|
Economy-overview: At independence in 1975, Mozambique was one of the world's poorest countries. Socialist mismanagement and a brutal civil war from 1977-92 exacerbated the situation. In 1987, the government embarked on a series of macroeconomic reforms designed to stabilize the economy. These steps, combined with donor assistance and with political stability since the multi-party elections in 1994, have led to dramatic improvements in the country's growth rate. Inflation was reduced to single digits during the late 1990s although it returned to double digits in 2000-06. Fiscal reforms, including the introduction of a value-added tax and reform of the customs service, have improved the government's revenue collection abilities. In spite of these gains, Mozambique remains dependent upon foreign assistance for much of its annual budget, and the majority of the population remains below the poverty line. Subsistence agriculture continues to employ the vast majority of the country's work force. A substantial trade imbalance persists although the opening of the Mozal aluminum smelter, the country's largest foreign investment project to date, has increased export earnings. In late 2005, and after years of negotiations, the government signed an agreement to gain Portugal's majority share of the Cahora Bassa Hydroelectricity (HCB) company, a dam that was not transferred to Mozambique at independence because of the ensuing civil war and unpaid debts. More power is needed for additional investment projects in titanium extraction and processing and garment manufacturing that could further close the import/export gap. Mozambique's once substantial foreign debt has been reduced through forgiveness and rescheduling under the IMF's Heavily Indebted Poor Countries (HIPC) and Enhanced HIPC initiatives, and is now at a manageable level. Labour force: 9.4 million (2006 est.) Labor force-by occupation: agriculture: 81%; industry: 6%; services: 13% (1997 est.) Unemployment rate: 21% (1997 est.) Population below poverty: 70% (2001 est.) Industries: food, beverages, chemicals (fertilizer, soap, paints), aluminum, petroleum products, textiles, cement, glass, asbestos, tobacco | |
|
Agricultural products: cotton, cashew nuts, sugarcane, tea, cassava (tapioca), corn, coconuts, sisal, citrus and tropical fruits, potatoes, sunflowers; beef, poultry Exports: $2.429 billion (f.o.b., 2006 est.) Exports-commodities: aluminum, prawns, cashews, cotton, sugar, citrus, timber; bulk electricity Exports-partners: Netherlands 59.7%, South Africa 16.2%, Zimbabwe 2.9% (2005) Imports: $2.815 billion (c.i.f., 2006 est.) Imports-commodities: machinery and equipment, vehicles, fuel, chemicals, metal products, foodstuffs, textiles Imports-partners: South Africa 42.9%, Netherlands 11.5%, Portugal 3.6% (2005) Currency: 1 metical (MZM) = 100 centavos Exchange rates: meticais per US dollar - 25.4 (2006), 23,061 (2005), 22,581 (2004), 23,782
(2003), 23,678 (2002) |
|
| back to top | |
|
Telephone system: fair system of
tropospheric scatter, open-wire lines, and microwave radio relay | |
| back to top | |
|
Purchase G. 2007. Mozambique: Preliminary Assessment of the Status and Distribution of Cheetah. Cat News Special Issue 3, 37-39. http://www.cia.gov/cia/publications/factbook/geos/mz.html (last update on 10 January, 2006) | |