|
|  |
| back to top | |
|
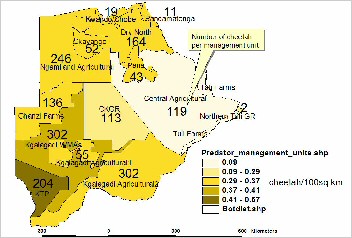
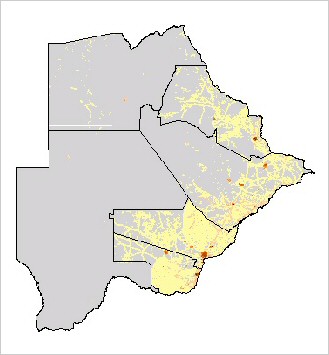
Population. Historically, cheetahs have been distributed throughout Botswana. With once pristine habitat, very low human populations and one of the largest concentrations of ungulates on the continent, space and prey were plentiful. However, the last 40 years have seen great changes in the natural habitat, with overstocking of livestock, range partitioning, the arrival of deep borehole technology and the erection of cordon fences causing dramatic reductions in wildlife populations and the overall integrity of the Kalahari ecosystems. Today, the population is estimated at 1,800 animals (Klein 2007).
Principal Threats. Livestock farming and poaching. |
|
| back to top | |
|
Formerly the British protectorate of Bechuanaland, Botswana adopted its new name upon independence in 1966. Four decades of uninterrupted civilian leadership, progressive social policies, and significant capital investment have created one of the most dynamic economies in Africa. Mineral extraction, principally diamond mining, dominates economic activity, though tourism is a growing sector due to the country's conservation practices and extensive nature preserves. Botswana has one of the world's highest known rates of HIV/AIDS infection, but also one of Africa's most progressive and comprehensive programs for dealing with the disease. | |
| back to top | |
|
Area: total: 600,370 sq km; land: 585,370 sq km; water: 15,000 sq km Climate: semiarid; warm winters and hot summers. Terrain: predominantly flat to gently rolling tableland; Kalahari Desert in southwest. Land use: arable land: 0.65%; permanent crops: 0.01%; other: 99.34% (2005) Natural resources: diamonds, copper, nickel, salt, soda ash, potash, coal, iron ore, silver. Natural hazards: periodic droughts; seasonal August winds blow from the west, carrying sand and dust across the country, which can obscure visibility. Environment-current issues: overgrazing; desertification; limited fresh water resources. Environment-international agreements: party to: Biodiversity, Climate
Change, Desertification, Endangered Species, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea,
Nuclear Test Ban, Ozone Layer Protection. |
|
|
|
|
| back to top | |
|
Population: 1,639,833 (July 2006 est.) Age structure: 0-14 years: 38.3% (male 319,531/female 309,074); 15-64 years: 57.9% (male 460,692/female 488,577); 65 years and over: 3.8% (male 23,374/female 38,585) (2006 est.) Median age: total: 19.4 years: male: 18.8 years; female: 20 years (2006 est.) Population growth rate: -0.04% (2006 est.) Infant mortality rate: total: 53.7 deaths/1,000 live births; male: 54.92 deaths/1,000 live births; female: 52.44 deaths/1,000 live births (2006 est.) Life expectancy at birth: total population: 33.74 years; male: 33.9 years; female: 33.56 years (2006 est.) Total fertility rate: 2.79 children born/woman (2006 est.) HIV/AIDS - adult prevalence rate: 37.3% (2003 est.) HIV/AIDS - people living with HIV/AIDS: 350,000 (2003 est.) HIV/AIDS - deaths: 33,000 (2003 est.) Major infectious diseases: food or waterborne diseases: bacterial diarrhea, hepatitis A, and typhoid fever; vectorborne disease: malaria (2007) |
|
|
Ethnic groups: Tswana (or Setswana) 79%, Kalanga 11%, Basarwa 3%, other, including Kgalagadi and white 7% Religions: Christian 71.6%, Badimo 6%, other 1.4%, unspecified 0.4%, none 20.6% (2001 census) Languages: Setswana 78.2%, Kalanga 7.9%, Sekgalagadi 2.8%, English 2.1% (official), other 8.6%, unspecified 0.4% (2001 census) Literacy: definition: age 15 and over can read and write: total population: 79.8%; male: 76.9%; female: 82.4% (2003 est.) |
|
| back to top | |
|
Data code: BC Government type: parliamentary republic Independence: 30 September 1966 (from UK) Legal system: based on Roman-Dutch law and local customary law; judicial review limited to matters of interpretation; has not accepted compulsory ICJ jurisdiction. | |
| back to top | ||
|
Economy-overview: Botswana has maintained one of the world's highest economic growth rates since independence in 1966, though growth has slowed to 4.7% in 2006. Through fiscal discipline and sound management, Botswana has transformed itself from one of the poorest countries in the world to a middle-income country with a per capita GDP of $11,200 in 2006. Two major investment services rank Botswana as the best credit risk in Africa. Diamond mining has fueled much of the expansion and currently accounts for more than one-third of GDP and for 70-80% of export earnings. Tourism, financial services, subsistence farming, and cattle raising are other key sectors. On the downside, the government must deal with high rates of unemployment and poverty. Unemployment officially was 23.8% in 2004, but unofficial estimates place it closer to 40%. HIV/AIDS infection rates are the second highest in the world and threaten Botswana's impressive economic gains. An expected leveling off in diamond mining production overshadows long-term prospects. Labor force: 288,400 formal sector employees (2004) Labor force-by occupation: 100,000 public sector; 135,000 private sector, including 14,300 who are employed in various mines in South Africa; most others engaged in cattle raising and subsistence agriculture (1995 est.) Unemployed: 40% (2005 est.) Population below poverty: 53% (2003) Industries: diamonds, copper, nickel, salt, soda ash, potash; livestock processing; textiles | ||
|
Agriculture-products: livestock, sorghum, maize, millet, beans, sunflowers, groundnuts Exports: $4.836 billion f.o.b. (2006 est.) Exports-commodities: diamonds, copper, nickel, soda ash, meat, textiles Exports-partners: EU 74%, Southern African Customs Union (SACU) 21%, Zimbabwe 3% (1996) Imports: $3.034 billion (f.o.b., 2006 est.) Imports-commodities: foodstuffs, machinery, electrical goods, transport equipment, textiles, fuel and petroleum products, wood and paper products, metal and metal products Imports-partners: Southern African Customs Union (SACU) 74%, EFTA 17%, Zimbabwe 4% (2004) Currency: 1 pula (P) = 100 thebe Exchange rates: pulas per US dollar - 5.8447 (2006), 5.1104 (2005), 4.6929 (2004), 4.9499 (2003), 6.3278 (2002) |
|
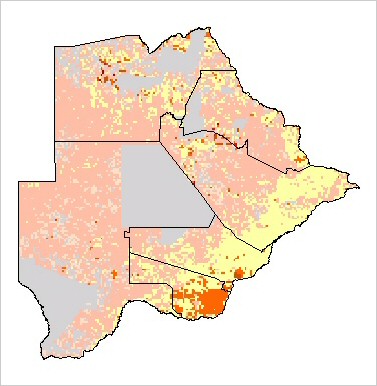
Distribution of bovine livestock in Botswana |
| back to top | |
|
Telephone system: general assessment: the system is expanding with the growth of mobile cellular service and participation in regional development; domestic: small system of open-wire lines, microwave radio relay links, and a few radiotelephone communication stations; mobile cellular service is growing fast; international: country code - 267; two international exchanges; digital microwave radio relay links to Namibia, Zambia, Zimbabwe, and South Africa; satellite earth station - 1 Intelsat (Indian Ocean) Radio broadcast stations: AM 8, FM 13, shortwave 4 (2001) Television broadcast stations: 1 (2001) Internet country code: .bw Internet hosts: 5,499 (2006) Internet users: 60,000 (2002) | |
| back to top | |
|
Klein R. 2007. Status Report for the Cheetah in Botswana. Cat News Special Issue 3, 14-21. Marker L., Malouf J. and Malouf A. 1999. Appendix 2: The status of the wild cheetah in its range countries. In: 1999 International Cheetah Studbook. http://www.cia.gov/cia/publications/factbook/geos/bw.html (last update on 10 January, 2006) http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Botswana http://www.lib.utexas.edu/maps/map_sites/country_sites.html#botswana | |