|
|
 |
| |
back to top | ||
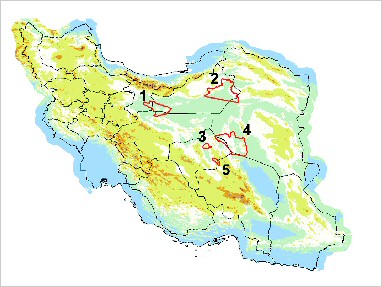
| Population: The Asiatic cheetah is on the verge of extinction with small populations remaining only in the Islamic Republic of Iran. Today, in the main desert areas around Dash-e-Kavir at the eastern half of the country, cheetah population is estimate to 60-100 individuals distributed in five areas. Some recent surveys conducted in Estahan and Yazd provinces revealed the presence of the Asiatic cheetah in four areas. Iran considers the cheetah an important part of its natural and cultural heritage and as such has become a symbol of its conservation efforts. Because the future of the cheetah is so precarious, Iran’s Dept. of the Environment launched a major initiative in conjunction with the UNDP-Global Environment Facility and the help of WCS to save the cheetah, its habitat, and prey. |
|
||
|
|
|||
|
|
|||
|
|||
| Known as Persia until 1935, Iran became an Islamic republic in 1979 after the ruling monarchy was overthrown and the shah was forced into exile. Conservative clerical forces established a theocratic system of government with ultimate political authority nominally vested in a learned religious scholar. Iranian-US relations have been strained since a group of Iranian students seized the US Embassy in Tehran on 4 November 1979 and held it until 20 January 1981. During 1980-88, Iran fought a bloody, indecisive war with Iraq that eventually expanded into the Persian Gulf and led to clashes between US Navy and Iranian military forces between 1987-1988. Iran has been designated a state sponsor of terrorism for its activities in Lebanon and elsewhere in the world and remains subject to US economic sanctions and export controls because of its continued involvement. Following the elections of a reformist president and Majlis in the late 1990s, attempts to foster political reform in response to popular dissatisfaction floundered as conservative politicians prevented reform measures from being enacted, increased repressive measures, and made electoral gains against reformers. Parliamentary elections in 2004 and the August 2005 inauguration of a conservative stalwart as president, completed the reconsolidation of conservative power in Iran's government. | |||
| |
back to top |
|
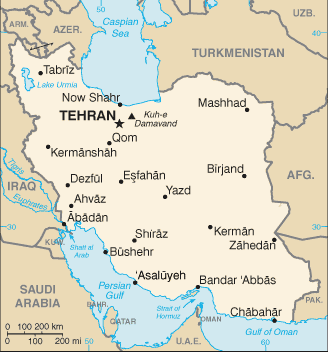
Area: total: 1.648 million sq km; land: 1.636 million sq km; water: 12,000 sq km Climate: mostly arid or semiarid, subtropical along Caspian coast Terrain: rugged, mountainous rim; high, central basin with deserts, mountains; small, discontinuous plains along both coasts Natural resources: petroleum, natural gas, coal, chromium, copper, iron ore, lead, manganese, zinc, sulfur Land use: arable land: 9.78%; permanent crops: 1.29%; other: 88.93% (2005) Irrigated land: 76,500 sq km (2003) Natural hazards: periodic droughts, floods; dust storms, sandstorms; earthquakes Environment - current issues: air pollution, especially in urban areas, from vehicle emissions, refinery operations, and industrial effluents; deforestation; overgrazing; desertification; oil pollution in the Persian Gulf; wetland losses from drought; soil degradation (salination); inadequate supplies of potable water; water pollution from raw sewage and industrial waste; urbanization Environment - international agreements: party to:
Biodiversity, Climate Change, Desertification, Endangered Species, Hazardous
Wastes, Marine Dumping, Ozone Layer Protection, Wetlands Geography - note: strategic location on the Persian Gulf and Strait of Hormuz, which are vital maritime pathways for crude oil transport |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
back to top | |
|
Population: 68,688,433 (July 2006 est.) Age structure:0-14 years: 26.1% (male 9,204,785/female 8,731,429); 15-64 years; % (male 24,133,919/female 23,245,255); 65 years and over: 4.9% (male 1,653,827/female Median age: total: 24.8 years; male: 24.6 years; female: 25 years (2006 est.) Population growth rate: 1.1% (2006 est.) Infant mortality rate: total: 40.3 deaths/1,000 live births; male: 40.49 deaths/1,000 live births; female: 40.1 deaths/1,000 live births (2006 est.) Life expectancy at birth: total population: 70.26 years; male: 68.86 years; female: 71.74 years (2006 est.) Total fertility rate: 1.8 children born/woman (2006 est.) HIV/AIDS - adult prevalence rate: less than 0.1% (2001 est.) HIV/AIDS - people living with HIV/AIDS: 31,000 (2001 est.) HIV/AIDS - deaths: 800 (2003 est.) |
|
|
|
|
|
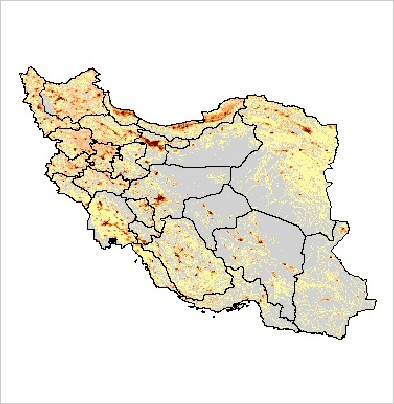
Distribution and density of the human population in Iran |
|
|
|
|
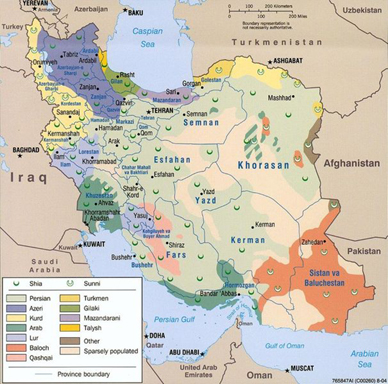
Ethnic groups: Persian 51%, Azeri 24%, Gilaki and Mazandarani 8%, Kurd 7%, Arab 3%, Lur 2%, Baloch 2%, Turkmen 2%, other 1% Religions: Shi'a Muslim 89%, Sunni Muslim 9%, Zoroastrian, Jewish, Christian, and Baha'i 2% Languages: Persian and Persian dialects 58%, Turkic and Turkic dialects 26%, Kurdish 9%, Luri 2%, Balochi 1%, Arabic 1%, Turkish 1%, other 2% Literacy: definition: age 15 and over can read and write; total population: 79.4%; male: 85.6%; female: 73% (2003 est.) |
|
|
|
|
|
Ethno-religious distribution in Iran |
| |
back to top |
|
Data code: IR Government type: theocratic republic Independence: 1 April 1979 (Islamic Republic of Iran proclaimed) Legal system: the Constitution codifies Islamic principles of government Political pressure groups and leaders: the Islamic Revolutionary Party (IRP) was Iran's sole political party until its dissolution in 1987; Iran now has a variety of groups engaged in political activity; some are oriented along political lines or based on an identity group; others are more akin to professional political parties seeking members and recommending candidates for office; some are active participants in the Revolution's political life while others reject the state; political pressure groups conduct most of Iran's political activities; groups that generally support the Islamic Republic include Ansar-e Hizballah, Muslim Students Following the Line of the Imam, Tehran Militant Clergy Association (Ruhaniyat), Islamic Coalition Party (Motalefeh), and Islamic Engineers Society; active pro-reform student groups include the Office of Strengthening Unity (OSU); opposition groups include Freedom Movement of Iran, the National Front, Marz-e Por Gohar, and various ethnic and Monarchist organizations; armed political groups that have been repressed by the government include Mujahidin-e Khalq Organization (MEK or MKO), People's Fedayeen, Democratic Party of Iranian Kurdistan (KDPI), and Komala. |
|
| back to top | |
|
Economy - overview: Iran's economy is marked by a bloated, inefficient state sector, over reliance on the oil sector, and statist policies that create major distortions throughout. Most economic activity is controlled by the state. Private sector activity is typically small-scale - workshops, farming, and services. President Mahmud AHMADI-NEJAD has continued to follow the market reform plans of former President RAFSANJANI, with limited progress. Relatively high oil prices in recent years have enabled Iran to amass nearly $60 billion in foreign exchange reserves, but have not eased economic hardships such as high unemployment and inflation. The proportion of the economy devoted to the development of weapons of mass destruction remains a contentious issue with leading Western nations. GDP - real growth rate: 5% (2006 est.) GDP - composition by sector: agriculture: 11.2%; industry: 41.7%; services: 47.1% (2006 est.) Labor force: 24.36 million; note: shortage of skilled labor (2006 est.) Labor force - by occupation: agriculture: 30%; industry: 25%; services: 45% (2001 est.) Unemployment rate: 11.2% (2004 est.) Population below poverty line: 40% (2002 est.) Agriculture - products: wheat, rice, other grains, sugar beets, fruits, nuts, cotton; dairy products, wool; caviar Industries: petroleum, petrochemicals, textiles, cement and other construction materials, food processing (particularly sugar refining and vegetable oil production), metal fabrication, armaments Industrial production growth rate: 3.2% excluding oil (2006 est.) Exports: $63.18 billion f.o.b. (2006 est.) Exports - commodities: petroleum 80%, chemical and petrochemical products, fruits and nuts, carpets Exports - partners: Japan 16.9%, China 11.2%, Italy 5.9%, South Korea 5.8%, Turkey 5.7%, Netherlands 4.6%, France 4.4%, South Africa 4.1%, Taiwan 4.1% (2005) Imports: $45.48 billion f.o.b. (2006 est.) Imports - commodities: industrial raw materials and intermediate goods, capital goods, foodstuffs and other consumer goods, technical services, military supplies Imports - partners: Germany 13.9%, UAE 8.4%, China 8.3%, Italy 7.1%, France 6.3%, South Korea 5.4%, Russia 4.9% (2005) Currency (code): Iranian rial (IRR) Exchange rates: rials per US dollar - 9,246.94 (2006), 8,964 (2005), 8,614 (2004), 8,193.9 (2003), 6,907 (2002), note, Iran has been using a managed floating exchange rate regime since unifying multiple exchange rates in March 2002 |
|
| back to top | |||
|
Telephone system: general assessment: inadequate, but currently being modernized and
expanded with the goal of not only improving the efficiency and increasing the
volume of the urban service but also bringing telephone service to several thousand
villages, not presently connected Radio broadcast stations: AM 72, FM 5, shortwave 5 (1998) Television broadcast stations: 28 (plus 450 low-power repeaters) (1997) Internet country code:ir Internet hosts: 5,242 (2006) Internet users: 7.5 million (2005) |
|||
|
|
|||
|
|||
|
Farhadinia MS. 2004. The last stronghold: cheetah in Iran. Anonymous. 2005. In Iran, camera traps reveal rare asiatic cheetahs. Hunter et al. 2006. Conserving the Asiatic Cheetah in Iran: Launching the First Radio-Telemetry Study. Cat News 46, 8-11. http://www.lib.utexas.edu/maps/iran.html |