|
|
 |
| back to top | |||
|
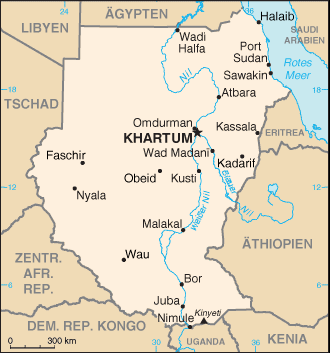
Population. Recent reports indicate that cheetah are mainly distributed in southern Sudan. In the north cheetah skins are used to make slippers and these are in great demand by rich Sudanese. Populations may still be present where adequate prey and livestock exist in semi-arid areas below the true desert in the central middle of the country. Widely distributed throughout the south, as of 1982. Recent information is lacking from the south of the country due to the long civil war. The population there could be greatly affected by the eight years of war. All wildlife has been severely affected by the availability of guns and ammunition. In the 1970s, cheetahs occurred in Southern National Park (23,000 km2), Boma National Park (22,800 km2), Boro Game Reserve (1,500 km2), Meshra Game Reserve (4,500 km2), Badingile Game Reserve (8,400 km2), Ashana Game Reserve (900 km2), Chelkou Game Reserve (5,500 km2), Kidepo Game Reserve (1,400km2), Numatina Game Reserve (2,100 km2), and Shambe Game Reserve (620 km2) (Hillman 1982). The cheetah has been a protected species since 1972. Effective 1 January 1989, Wildlife Conservation and National Park forces of Sudan issued a 3-year notice banning the hunting and capture of mammals, birds and reptiles in the Republic of Sudan. Principal Threats. Poaching, loss of prey,
indirect affects of the long civil war in the south of the country.
|
|||
|
|
|||
| Military regimes favoring Islamic-oriented governments have dominated national politics since independence from the UK in 1956. Sudan was embroiled in two prolonged civil wars during most of the remainder of the 20th century. These conflicts were rooted in northern economic, political, and social domination of largely non-Muslim, non-Arab southern Sudanese. The first civil war ended in 1972, but broke out again in 1983. The second war and famine-related effects resulted in more than 4 million people displaced and, according to rebel estimates, more than 2 million deaths over a period of two decades. Peace talks gained momentum in 2002-04 with the signing of several accords. The final North/South Comprehensive Peace Agreement (CPA), signed in January 2005, granted the southern rebels autonomy for six years, after which a referendum for independence is scheduled to be held. A separate conflict that broke out in the western region of Darfur in 2003 has displaced nearly 2 million people and caused an estimated 200,000 to 400,000 deaths. As of late 2006, peacekeeping troops were struggling to stabilize the situation, which has become increasingly regional in scope, and has brought instability to eastern Chad, and Sudanese incursions into the Central African Republic. Sudan also has faced large refugee influxes from neighboring countries, primarily Ethiopia and Chad, and armed conflict, poor transport infrastructure, and lack of government support have chronically obstructed the provision of humanitarian assistance to affected populations. | |||
| back to top | |
|
Area: total: 2,505,810 sq km; land: 2.376 million sq km; water: 129,810 sq km Climate:
tropical in south; arid desert in north; rainy season (April to October) Land use: arable land: 6.78%; permanent crops: 0.17%; other: 93.05% (2005) Natural resources: petroleum; small reserves of iron ore, copper, chromium ore, zinc, tungsten, mica, silver, gold Irrigated land: 19,460 sq km (1993 est.) Natural hazards: dust storms Environment-current issues: inadequate supplies of potable water; wildlife populations threatened by excessive hunting; soil erosion; desertification Environment-international agreements: | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| back to top | |
|
Population: 41,236,378 (July 2006 est.) Age structure: 0-14 years: 42.7% (male 8,993,483/female 8,614,022); 15-64 years: 54.9% (male 11,327,679/female 11,297,798); 65 years and over: 2.4% (male 536,754/female 466,642) (2006 est.) Median age: total: 18.3 years; male: 18.1 years; female: 18.5 years (2006 est.) Population growth rate: 2.55% (2006 est.) Infant mortality rate: total: 61.05 deaths/1,000 live births; male: 61.88 deaths/1,000 live births; female: 60.18 deaths/1,000 live births (2006 est.) Life expectancy at birth: total population: 58.92 years; male: 57.69 years; female: 60.21 years (2006 est.) Total fertility rate: 4.72 children born/woman (2006 est.) |
|
|
HIV/AIDS - adult prevalence rate: 2.3% (2001 est.) Distribution of the human population in Sudan HIV/AIDS - people living with HIV/AIDS: 400,000 (2001 est.) HIV/AIDS - deaths: 23,000 (2003 est.) Ethnic groups: black 52%, Arab 39%, Beja 6%, foreigners 2%, other 1% Religions: Sunni Muslim 70% (in north), indigenous beliefs 25%, Christian 5% (mostly in south and Khartoum) Languages: Arabic (official), Nubian, Ta Bedawie, diverse dialects of Nilotic, Nilo-Hamitic, Sudanic languages, English Literacy: definition: age 15 and over can read and write; total population: 61.1%; male: 71.8%; female: 50.5% (2003 est.) |
|
| back to top | |
|
Data code: SU Government type: transitional-previously ruling military junta; presidential and National Assembly elections held in March 1996; new constitution drafted by Presidential Committee, went into effect on 30 June 1998 after being approved in nationwide referendum Independence: 1 January 1956 (from Egypt and UK) Legal system: based on English common law and Islamic law; as of 20 January 1991, the now defunct Revolutionary Command Council imposed Islamic law in the northern states; Islamic law applies to all residents of the northern states regardless of their religion; however, the CPA establishes some protections for non-Muslims in Khartoum; some separate religious courts; accepts compulsory ICJ jurisdiction, with reservations; the southern legal system is still developing under the CPA following the civil war; Islamic law will not apply to the southern states Political pressure groups and leaders: Umma Party [Sadiq al-MAHDI]; Popular Congress Party or PCP [Hassan al-TURABI] |
|
| back to top | |
|
Economy-overview: Sudan has turned around a struggling economy with sound economic policies and infrastructure investments, but it still faces formidable economic problems, starting from its low level of per capita output. From 1997 to date, Sudan has been implementing IMF macroeconomic reforms. In 1999, Sudan began exporting crude oil and in the last quarter of 1999 recorded its first trade surplus, which, along with monetary policy, has stabilized the exchange rate. Increased oil production, high oil prices, revived light industry, and expanded export processing zones helped sustain GDP growth at 10% in 2006. Agricultural production remains Sudan's most important sector, employing 80% of the work force and contributing 35% of GDP, but most farms remain rain-fed and susceptible to drought. Chronic instability - resulting from the long-standing North/South civil war as well as the Darfur conflict, adverse weather, and weak world agricultural prices - ensure that much of the population will remain at or below the poverty line for years. In late 2006 the government announced its intention to introduce a new currency, the Sudan Pound, from January 2007, at an exchange rate of $1.00 = 2 Sudanese Pounds. GDP - real growth rate: 9.6% (2006 est.) GDP - composition by sector: agriculture: 35.5%; industry: 24.8%; services: 39.7% (2006 est.) Labor force: 7.415
million (1996 est.) Unemployment rate: 18.7% (2002 est.) Population below poverty line: 40% (2004 est.) Industries: cotton ginning, textiles, cement, edible oils, sugar, soap distilling, shoes, petroleum refining Industrial production growth rate: 8.5% (1999 est.) |
|
|
Agriculture-products: cotton, groundnuts (peanuts), sorghum, millet, wheat, gum arabic, sesame; sheep Exports: $594 million (f.o.b., 1997) Exports-commodities: cotton 23%, sesame 22%, livestock/meat 13%, gum arabic 5% (1996) Exports-partners: Saudi Arabia 20%, UK 14%, China 11%, Italy 8% (1996) Imports: $1.42 billion (f.o.b., 1997) Imports-commodities: foodstuffs, petroleum products, manufactured goods, machinery and equipment, medicines and chemicals, textiles (1996) Imports-partners: Saudi Arabia 10%, South Korea 7%, Germany 6%, Egypt 6% (1996) |
|
|
Currency: 1 Sudanese pound (£Sd) = 100 piastres Exchange rates: Sudanese pounds (£Sd) per US$1-1,819.70 (April 1998), 1,873.53 (2d Qtr 1998), 1,575.74 (1997), 1,250.79 (1996), 580.87 (1995), 289.61 (1994), 159.31 (1993) |
|
| back to top | |
|
Telephone system:
large, well-equipped system by African standards, but barely adequate and
poorly maintained by modern standards Radio broadcast stations: AM 11, FM 1, shortwave 1 (1998 est.) Television broadcast stations: 3 (1997) Internet country code: .sd Internet hosts: 16 (2006) Internet users: 2.8 million (2005) |
|
| back to top |
|
Marker L., Malouf J. and Malouf A. 1999. Appendix 2: The status of the wild cheetah in its range countries. In: 1999 International Cheetah Studbook. http://www.lib.utexas.edu/maps/sudan.html |