|
|
| |
back to top | ||
|
Population. No current information. Possibly still a few animals in Parc National Du Niokolo-Koba (8,000km2). Principal Threats. Lack of habitat. |
|||
|
|
|||
|
|||
|
Independent from France in 1960, Senegal was ruled by the Socialist Party for forty years until current President Abdoulaye WADE was elected in 2000. Senegal joined with The Gambia to form the nominal confederation of Senegambia in 1982, but the envisaged integration of the two countries was never carried out, and the union was dissolved in 1989. The most significant threat within Senegal since the 1980s has been led by the Movement of Democratic Forces in the Casamance (MFDC). Although a peace agreement was signed in December 2004, internal rifts continue to keep the peace process deadlocked. Nevertheless, Senegal remains one of the most stable democracies in Africa. Senegal has a long history of participating in international peacekeeping. |
|||
| |
back to top |
|
Area: total: 196,190 sq km; land: 192,000 sq km; water: 4,190 sq km Climate: tropical; hot, humid; rainy season (May to November) has strong southeast winds; dry season (December to April) dominated by hot, dry, harmattan wind Terrain: generally low, rolling, plains rising to foothills in southeast Natural resources: fish, phosphates, iron ore Land use: arable land: 12.51%; permanent crops: 0.24%; other: 87.25% (2005) Irrigated land: 1,200 sq km (2003) Natural hazards: lowlands seasonally flooded; periodic droughts Environment - current issues: wildlife populations threatened by poaching; deforestation; overgrazing; soil erosion; desertification; overfishing Environment -
international agreements: party
to: Biodiversity,
Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered
Species, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Marine Life Conservation, Ozone
Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Wetlands, Whaling
|
|
|
|
|
| |
back to top |
|
Population: 11,987,121 (July 2006 est.) Age structure: 0-14 years: 40.8% (male 2,467,021/female 2,422,385); 15-64 years: 56.1% (male 3,346,756/female 3,378,518); 65 years and over: 3.1% (male 174,399/female 198,042) (2006 est.) Median age: total: 19.1 years; male: 18.9 years; female: 19.3 years (2006 est.) Population growth rate: 2.34% (2006 est.) Infant mortality rate: total: 52.94 deaths/1,000 live births; male: 56.49 deaths/1,000 live births; female: 49.29 deaths/1,000 live births (2006 est.) est.) Life expectancy at birth: total population: 59.25 years; male: 57.7 years; female: 60.85 years (2006 est.) Total fertility rate: 4.38 children born/woman (2006 est.) |
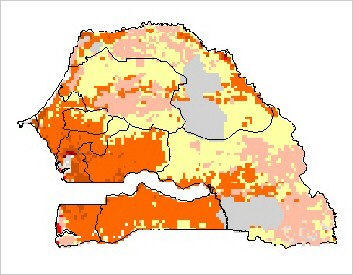
 Distribution of the human population in Senegal |
|
HIV/AIDS - adult prevalence rate: 0.8% (2003 est.) HIV/AIDS - people living with HIV/AIDS: 44,000 (2003 est.) HIV/AIDS - deaths: 3,500 (2003 est.) Ethnic groups: Wolof 43.3%, Pular 23.8%, Serer 14.7%, Jola 3.7%, Mandinka 3%, Soninke 1.1%, European and Lebanese 1%, other 9.4% Religions: Muslim 94%, Christian 5% (mostly Roman Catholic), indigenous beliefs 1% Languages: French (official), Wolof, Pulaar, Jola, Mandinka Literacy: definition: age 15 and over can read and write; total population: 40.2%; male: 50%; female: 30.7% (2003 est.) |
|
| |
back to top |
|
Data Code: SN Government type: republic Independence: 4 April 1960 (from France); note - complete independence achieved upon dissolution of federation with Mali on 20 August 1960 Legal system: based on French civil law system; judicial review of legislative acts in Constitutional Court; the Council of State audits the government's accounting office; accepts compulsory ICJ jurisdiction, with reservations Political pressure groups and leaders: labor; Sufi and Mouride brotherhoods; students; teachers |
|
| |
back to top |
|
Economy - overview: In January 1994, Senegal undertook a bold and ambitious economic reform program with the support of the international donor community. This reform began with a 50% devaluation of Senegal's currency, the CFA franc, which was linked at a fixed rate to the French franc. Government price controls and subsidies have been steadily dismantled. After seeing its economy contract by 2.1% in 1993, Senegal made an important turnaround, thanks to the reform program, with real growth in GDP averaging over 5% annually during 1995-2006. Annual inflation had been pushed down to the low single digits. As a member of the West African Economic and Monetary Union (WAEMU), Senegal is working toward greater regional integration with a unified external tariff and a more stable monetary policy. High unemployment, however, continues to prompt illegal migrants to flee Senegal in search of better job opportunities in Europe. Senegal was also beset by an energy crisis that caused widespread blackouts in 2006. Senegal still relies heavily upon outside donor assistance. Under the IMF's Highly Indebted Poor Countries (HIPC) debt relief program, Senegal will benefit from eradication of two-thirds of its bilateral, multilateral, and private-sector debt. GDP - real growth rate: 4.9% (2006 est.) GDP - composition by sector: agriculture: 18.3%; industry: 19.2%; services: 62.5% (2006 est.) Labor force: 4.749 million (2006 est.) Labor force - by occupation: agriculture: 77%; industry and services: 23% (1990 est.) Unemployment rate: 48%; note - urban youth 40% (2001 est.) Population below poverty line: 54% (2001 est.) |
|
|
Agriculture - products: peanuts, millet, corn, sorghum, rice, cotton, tomatoes, green vegetables; cattle, poultry, pigs; fish Industries: agricultural and fish processing, phosphate mining, fertilizer production, petroleum refining, construction materials, ship construction and repair Industrial production growth rate: 3.2% (2006 est.) Exports: $1.478 billion f.o.b. (2006 est.) Exports - commodities: fish, groundnuts (peanuts), petroleum products, phosphates, cotton Exports - partners: Mali 16.9%, India 13.1%, France 9.5%, Spain 6.1%, Italy 5.5%, Gambia, The 4.6% (2005) Imports: $2.98 billion f.o.b. (2006 est.) Imports - commodities: food and beverages, capital goods, fuels |
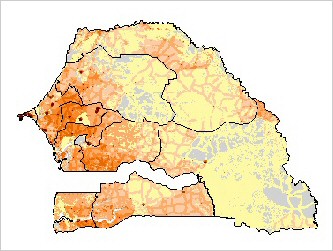
Distribution of bovine livestock in Senegal |
|
Imports - partners: France 22.8%, Nigeria 11.4%, Brazil 4.5%, Thailand 4.3%, US 4.2%, UK 4% (2005) Currency (code): Communaute Financiere Africaine franc (XOF); note - responsible authority is the Central Bank of the West African States Exchange rates: Communaute Financiere Africaine francs (XOF) per US dollar - 522.89 (2006), 527.47 (2005), 528.29 (2004), 581.2 (2003), 696.99 (2002) |
|
| |
back to top |
|
Telephone system: general assessment: good system; domestic: above-average urban system; microwave radio relay, coaxial cable and fiber-optic cable in trunk system; international: country code - 221; 4 submarine cables; satellite earth station - 1 Intelsat (Atlantic Ocean) Radio broadcast stations: AM 8, FM 20, shortwave 1 (2001) Television broadcast stations: 1 (1997) Internet country code: .sn Internet hosts: 412 (2006) Internet users: 540,000 (2005) |
|
| |
back to top |
|
Marker L., Malouf J. and Malouf A.1999. Appendix 2: The status of the wild cheetah in its range countries. In: 1999 International Cheetah Studbook. http://www.lib.utexas.edu/maps/senegal.html |