|
|
 |
| |
back to top | ||
|
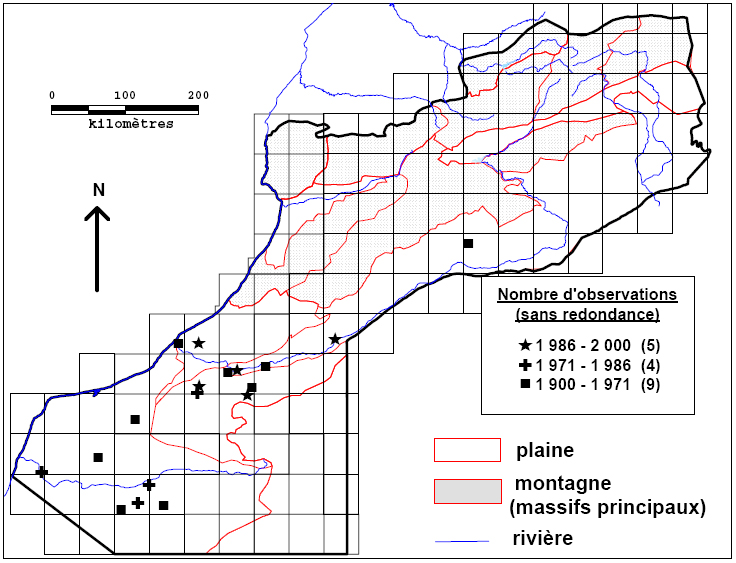
Pooulation. It has been considered extinct, but a recent investigation suggests that there are some 20 individuals mainly located along mined Saharan defence walls. Cheetahs have lived probably until the late 1970's in the thorn bush plains, from the Moroccan part of the Ora' Hamada' (Hamada du Draa) to the Moroccan pan of the Gir Hamada (Hamada du Guir), SE of the country along the Algerian border. Population History. In the 19th century cheetahs were present in S Morocco from the shores of the Atlantic ocean in the west to the Algerian border in the East and from the Western Sahara border in the south to the high Alfalfa steppes of the south pan of the High Atlas (Haut Atlas) in the north. French zoologist L.G. Seurat (1943) wrote about the appearance of 12 cheetahs in the Moroccan Gir Hamada near Figig (Figuig). |
Cheetah records in Morocco (Cuzin 2003) |
||
|
|
|||
|
|||
|
In 788, about a century after the Arab conquest of North Africa, successive Moorish dynasties began to rule in Morocco. In the 16th century, the Sa'adi monarchy, particularly under Ahmad AL-MANSUR (1578-1603), repelled foreign invaders and inaugurated a golden age. In 1860, Spain occupied northern Morocco and ushered in a half century of trade rivalry among European powers that saw Morocco's sovereignty steadily erode; in 1912, the French imposed a protectorate over the country. A protracted independence struggle with France ended successfully in 1956. The internationalized city of Tangier and most Spanish possessions were turned over to the new country that same year. Morocco virtually annexed Western Sahara during the late 1970s, but final resolution on the status of the territory remains unresolved. Gradual political reforms in the 1990s resulted in the establishment of a bicameral legislature, which first met in 1997. Lower house elections were last held held in September 2002 and upper house elections were last held in September 2006. |
|||
| |
back to top | |
|
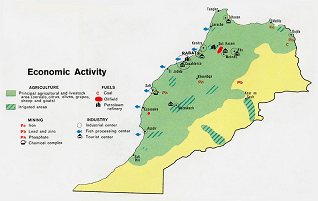
Area: total: 446,550 sq km; land: 446,300 sq km; water: 250 sq km Climate: Mediterranean, becoming more extreme in the interior Terrain: northern coast and interior are mountainous with large areas of bordering plateaus, intermontane valleys, and rich coastal plains Natural resources: phosphates, iron ore, manganese, lead, zinc, fish, salt Land use: arable land: 19%; permanent crops: 2%; other: 79% (2005) Irrigated land: 14,450 sq km (2003) Natural hazards: northern mountains geologically unstable and subject to earthquakes; periodic droughts Environment - current issues: land degradation/desertification (soil erosion resulting from farming of marginal areas, overgrazing, destruction of vegetation); water supplies contaminated by raw sewage; siltation of reservoirs; oil pollution of coastal waters Environment -
international agreements: party
to: Biodiversity,
Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered
Species, Hazardous Wastes, Marine Dumping, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship
Pollution, Wetlands, Whaling; signed, but not ratified: Environmental
Modification, Law of the Sea |
||
|
|
|
|
| |
back to top | |
|
Population: 33,241,259 (July 2006 est.) Age structure: 0-14 years: 31.6% (male 5,343,976/female 5,145,019); 15-64 years: 63.4% (male 10,505,018/female 10,580,599); 65 years and over: 5% (male 725,116/female 941,531) (2006 est.) Median age: total: 23.9 years; male: 23.4 years; female: 24.5 years (2006 est.) Population growth rate: 1.55% (2006 est.) Infant mortality rate: total: 40.24 deaths/1,000 live births; male: 43.99 deaths/1,000 live births; female: 36.3 deaths/1,000 live births (2006 est.) Life expectancy at birth: total population: 70.94 years; male: 68.62 years; female: 73.37 years (2006 est.) Total fertility rate: 2.68 children born/woman (2006 est.) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
HIV/AIDS - adult prevalence rate: 0.1% (2001 est.) HIV/AIDS - people living with HIV/AIDS: 15,000 (2001 est.) HIV/AIDS - deaths: NA Ethnic groups: Arab-Berber 99.1%, other 0.7%, Jewish 0.2% Religions: Muslim 98.7%, Christian 1.1%, Jewish 0.2% Languages: Arabic (official), Berber dialects, French often the language of business, government, and diplomacy Literacy: definition: age 15 and over can read and write; total population: 51.7%; male: 64.1%; female: 39.4% (2003 est.) |
|
|
||
| |
back to top |
|
Data Code: MA Government type: constitutional monarchy Independence: 2 March 1956 (from France) Legal system: based on Islamic law and French and Spanish civil law system; judicial review of legislative acts in Constitutional Chamber of Supreme Court Political pressure groups and leaders: Democratic Confederation of Labor or CDT [Noubir AMAOUI]; General Union of Moroccan Workers or UGTM [Abderrazzak AFILAL]; Moroccan Employers Association or CGEM [Hassan CHAMI]; National Labor Union of Morocco or UNMT [Abdelslam MAATI]; Union of Moroccan Workers or UMT [Mahjoub BENSEDDIK] |
|
| |
back to top |
|
Economy - overview: Moroccan economic policies brought macroeconomic stability to the country in the early 1990s but have not spurred growth sufficient to reduce unemployment that nears 20% in urban areas. Poverty has increased due to the volatile nature of GDP, Morocco's continued dependence on foreign energy, and its inability to promote the growth of small and medium size enterprises. However, GDP growth rebounded to 6.7% in 2006 due to high rainfall, which resulted in a strong second harvest. Despite structural adjustment programs supported by the IMF, the World Bank, and the Paris Club, the dirham is only fully convertible for current account transactions and Morocco's financial sector is rudimentary. |
|
|
Moroccan authorities understand that reducing poverty and providing jobs is key to domestic security and development. In 2004, Moroccan authorities instituted measures to boost foreign direct investment and trade by signing a free trade agreement with the US, which entered into force in January 2006, and sold government shares in the state telecommunications company and in the largest state-owned bank. Long-term challenges include preparing the economy for freer trade with the US and European Union, improving education and job prospects for Morocco's youth, and raising living standards, which the government hopes to achieve by increasing tourist arrivals and boosting competitiveness in textiles. |
|
|
GDP - real growth rate: 6.7% (2006 est.) GDP - composition by sector: agriculture: 13.3%; industry: 31.2%; services: 55.5% (2006 est.) Labor force: 11.25 million (2006 est.) Labor force - by occupation: agriculture: 40%; industry: 15%; services: 45% (2003 est.) Unemployment rate: 7.7% (2006 est.) Population below poverty line: 19% (2005 est.) Agriculture - products: barley, wheat, citrus, wine, vegetables, olives; livestock Industries: phosphate rock mining and processing, food processing, leather goods, textiles, construction, tourism Industrial production growth rate: 4% (2004 est.) Exports: $11.72 billion f.o.b. (2006 est.) Exports - commodities: clothing, fish, inorganic chemicals, transistors, crude minerals, fertilizers (including phosphates), petroleum products, fruits, vegetables Exports - partners: France 30.3%, Spain 18%, UK 6.2%, Italy 5.2%, India 4.1% (2005) Imports: $21.22 billion f.o.b. (2006 est.) Imports - commodities: crude petroleum, textile fabric, telecommunications equipment, wheat, gas and electricity, transistors, plastics Imports - partners: France 18.2%, Spain 11%, Saudi Arabia 6.8%, Russia 6.8%, Italy 6.1%, China 5.2%, Germany 4.7% (2005) Currency (code): Moroccan dirham (MAD) Exchange rates: Moroccan dirhams per US dollar - 8.7722 (2006), 8.865 (2005), 8.868 (2004), 9.574 (2003), 11.021 (2002) |
|
| |
back to top |
|
Telephone system: general
assessment: modern system with all important capabilities;
however, density is low with only 4 main lines available for each 100 persons Radio broadcast stations: AM 27, FM 25, shortwave 6 (1998) Television broadcast stations: 35 (plus 66 repeaters) (1995) Internet country code: .ma Internet hosts: 3,218 (2006) Internet users: 4.6 million (2005)
|
|
| back to top |
|
Marker L., Malouf J. and Malouf A. 1999. Appendix 2: The status of the wild cheetah in its range countries. In: 1999 International Cheetah Studbook. Cuzin F. 2003. The Cheetah Acynonyx jubatus in Morocco. O’Mopsan L. K.1998. The 1996 International Cheetah Studbook - an updated status report http://www.lib.utexas.edu/maps/morocco.html |