|
|
 |
| back to top | |||
|
Population. Estimated at 100. Once widely distributed, now relict populations perhaps survive in parts of Gaza and Inhambane Provinces and south of the Zambezi River, and in the southern regions of Tete Province. The Tete Region is believed to be absent of cheetah now. The Gorongoza National Park (3,770 km2) had a small population of cheetah. Principal Threats. Poaching due to civil war situation, lack of enforced protection. |
|||
|
|
|||
|
|||
|
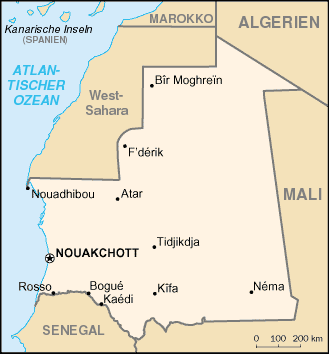
Independent from France in 1960, Mauritania annexed the southern third of the former Spanish Sahara (now Western Sahara) in 1976, but relinquished it after three years of raids by the Polisario guerrilla front seeking independence for the territory. Maaouya Ould Sid Ahmed TAYA seized power in a coup in 1984. Opposition parties were legalized and a new constitution approved in 1991. Two multiparty presidential elections since then were widely seen as flawed, but October 2001 legislative and municipal elections were generally free and open. A bloodless coup in August 2005 deposed President TAYA and ushered in a military council headed by Col. Ely Ould Mohamed VALL, which declared it would remain in power for up to two years while it created conditions for genuine democratic institutions and organized elections. Accordingly, parliamentary elections were held in December of 2006 and senatorial and presidential elections will follow (January and March 2007 respectively). The newly-elected legislature is expected to assume power following the inauguration of the new president. For now, however, Mauritania remains an autocratic state, and the country continues to experience ethnic tensions among its black population and different Moor (Arab-Berber) communities. |
|||
| back to top | |
|
Area: total: 1,030,700 sq km; land: 1,030,400 sq km; water: 300 sq km Climate:
tropical; hot, humid in south; semiarid in north Natural resources: phosphates, limestone, marble Land use: arable land: 0.2%; permanent crops: 0.01%; other: 99.79% (2005) Irrigated land: 490 sq km (2002) Natural hazards: hot, dry harmattan wind can reduce visibility in north during winter; periodic droughts Environment-current issues: deforestation attributable to slash-and-burn agriculture and the use of wood for fuel; recent droughts affecting agriculture Environment-international agreements: | |
|
|
|
| back to top | ||
|
Population: 3,177,388 (July 2006 est.) Age structure: 0-14 years: 45.6% (male 726,376/female 723,013); 15-64 years: 52.2% (male 818,408/female 839,832); 65 years and over: 2.2% (male 28,042/female 41,717) (2006 est.) Median age: total: 17 years; male: 16.8 years; female: 17.3 years (2006 est.) Population growth rate: 2.88% (2006 est.) Infant mortality rate: total: 69.48 deaths/1,000 live births; male: 72.44 deaths/1,000 live births; female: 66.43 deaths/1,000 live births (2006 est.) Life expectancy at birth: total population: 53.12 years; male: 50.88 years; female: 55.42 years (2006 est.) Total fertility rate: 5.86 children born/woman (2006 est.) |
|
|
|
HIV/AIDS - adult prevalence rate: 0.6% (2003 est.) HIV/AIDS - people living with HIV/AIDS: 9,500 (2003 est.) HIV/AIDS - deaths: less than 500 (2003 est.) Ethnic groups: native African (37 tribes; largest and most important are Ewe, Mina, and Kabre) 99%, European and Syrian-Lebanese less than 1% Religions: indigenous beliefs 70%, Christian 20%, Muslim 10% Languages: French (official and the language of commerce), Ewe and Mina (the two major African languages in the south), Kabye (sometimes spelled Kabiye) and Dagomba (the two major African languages in the north) Literacy: definition: age 15 and over can read and write; total population: 41.7%; male: 51.8%; female: 31.9% (2003 est.) |
||
| back to top | |
|
Data code: TO Government type: republic under transition to multiparty democratic rule Independence: 27 April 1960 (from French-administered UN trusteeship) Legal system: French-based court system |
|
|
|
|
| back to top | ||
|
Economy-overview: This small sub-Saharan economy is heavily dependent on both commercial and subsistence agriculture, which provides employment for 65% of the labor force. Cocoa, coffee, and cotton together generate about 30% of export earnings. Togo is self-sufficient in basic foodstuffs when harvests are normal, with occasional regional supply difficulties. In the industrial sector, phosphate mining is by far the most important activity, although it has suffered from the collapse of world phosphate prices and increased foreign competition. Togo serves as a regional commercial and trade center. The government's decade-long effort, supported by the World Bank and the IMF, to implement economic reform measures, encourage foreign investment, and bring revenues in line with expenditures has stalled. Political unrest, including private and public sector strikes throughout 1992 and 1993, jeopardized the reform program, shrunk the tax base, and disrupted vital economic activity. The 12 January 1994 devaluation of the currency by 50% provided an important impetus to renewed structural adjustment; these efforts were facilitated by the end of strife in 1994 and a return to overt political calm. Progress depends on following through on privatization, increased transparency in government accounting to accommodate increased social service outlays, and possible downsizing of the military, on which the regime has depended to stay in place. However, in late 1998 the EU suspended aid and trade preferences for Togo because of grave doubts over the conduct of the presidential elections. The World Bank also suspended its disbursements at yearend 1998 because Togo was unable to pay its arrears. GDP - real growth rate: 19.4% (2006 est.) GDP - composition by sector: agriculture: 25%; industry: 29%; services: 46% (2001 est.) Labor force: 786,000 (2001) Labor force-by occupation: agriculture 65%, industry 5%, services 30% (1998 est.) Unemployment rate: 20% (2004 est.) Population below poverty line: 40% (2004 est.) Industries: phosphate mining, agricultural processing, cement; handicrafts, textiles, beverages Industrial production growth rate: 2% (2000 est.) |
||
|
Agriculture-products: coffee, cocoa, cotton, yams, cassava (tapioca), corn, beans, rice, millet, sorghum; livestock; fish Exports: $345 million (f.o.b., 1997) Exports-commodities: cotton, phosphates, coffee, cocoa Exports-partners: Canada 7.6%, Taiwan 7.1%, Nigeria 6.8%, South Africa 5.2% (1996 est.) Imports: $400 million (f.o.b., 1997) Imports-commodities: machinery and equipment, consumer goods, petroleum products Imports-partners: Ghana 19.1%, France 10.8%, China 8.2%, Cameroon 6.8% (1996 est.) Currency: 1 Communaute Financiere Africaine franc (CFAF) = 100 centimes Exchange rates: Communaute Financiere Africaine francs (CFAF) per US$1-560.01 (December 1998), 589.95 (1998), 583.67 (1997), 511.55 (1996), 499.15 (1995), 555.20 (1994) |
|
|
| back to top | |
|
Telephone
system: fair system based on network of microwave radio relay
routes supplemented by open-wire lines and cellular system Radio broadcast stations: AM 2, FM 0, shortwave 0 Television broadcast stations: 3 (in addition, there are two repeaters) (1997) Internet country code: .mr Internet hosts: 32 (2006) Internet users: 14,000 (200 |
|
| back to top |
|
Marker L., Malouf J. and Malouf A. 1999. Appendix 2: The status of the wild cheetah in its range countries. In: 1999 International Cheetah Studbook. http://www.lib.utexas.edu/maps/mauritania.html |