|
|
 |
| back to top | ||||
|
|
|
|||
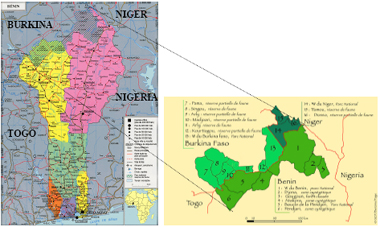
| Population. Cheetahs are thought to be extinct outside of the tri-country national park in the north of Benin, the Park Nationale du W, which adjoins Niger, Burkina Faso and Benin. In this park, a small population exists. Cheetahs also exist in and around the Pendjari complex of protected areas in northwestern Benin. Between December 2001 and April 2004, 24 cheetah observations have been reported by tourists, mostly along the Pendjari river (North Benin), where tourist activities are concentrated (Claro & Helder 2004). Berzins et al. (2007) investigated the presence of cheetahs in the Pendjari Biosphere Reserve PBR and the W Benin with interviews. In the PBR, 10 observations were made during 2005. In W Benin, park wardens have observed cheetahs 21 times in between 2000-2006. |
|
Tri-country W National Park |
||
|
Principal Threat. Insufficient numbers of cheetah to sustain a viable population and lack of habitat. |
||||
|
|
||||
|
|
||||
| Present day Benin was the site of Dahomey, a prominent West African kingdom that rose in the 15th century. The territory became a French Colony in 1872 and achieved independence on 1 August 1960, as the Republic of Benin. A succession of military governments ended in 1972 with the rise to power of Mathieu KEREKOU and the establishment of a government based on Marxist-Leninist principles. A move to representative government began in 1989. Two years later, free elections ushered in former Prime Minister Nicephore SOGLO as president, marking the first successful transfer of power in Africa from a dictatorship to a democracy. KEREKOU was returned to power by elections held in 1996 and 2001, though some irregularities were alleged. KEREKOU stepped down at the end of his second term in 2006 and was succeeded by Thomas YAYI BONI, a political outsider and independent. | ||||
| |
back to top | |
|
Area: total: 112,620 sq km; land: 110,620 sq km; water: 2,000 sq km Climate: tropical; hot, humid in south; semiarid in north Terrain: mostly flat to undulating plain; some hills and low mountains Natural resources: small offshore oil deposits, limestone, marble, timber Land use: arable land: 23.53%; permanent crops: 2.37%; other: 74.1% (2005) Irrigated land: 120 sq km (2003) Natural hazards: hot, dry, dusty harmattan wind may affect north from December to March Environment - current issues: inadequate supplies of potable water; poaching threatens wildlife populations; deforestation; desertification Environment - international agreements: party to:
Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification,
Endangered Species, Environmental Modification, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the
Sea, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Wetlands; signed, but not
ratified: none of the selected agreements |
||
|
|
|
|
| |
back to top |
|
Population: 7,862,944 Age structure: 0-14 years: 44.1% (male 1,751,709/female 1,719,138); 15-64 years: 53.5% (male 2,067,248/female 2,138,957); 65 years and over: 2.4% (male 75,694/female 110,198) (2006 est.) Median age: total: 17.6 years; male: 17.2 years; female: 18 years (2006 est.) Population growth rate: 2.73% (2006 est.) Infant mortality rate: total: 79.56 deaths/1,000 live births; male: 84.09 deaths/1,000 live births; female: 74.88 deaths/1,000 live births (2006 est.) Life expectancy at birth: total population: 53.04 years; male: 51.9 years; female: 54.22 years (2006 est.) Total fertility rate: 5.2 children born/woman (2006 est.)
|
|
|
HIV/AIDS - adult prevalence rate: 1.9% (2003 est.) HIV/AIDS - people living with HIV/AIDS: 68,000 (2003 est.) HIV/AIDS - deaths: 5,800 (2003 est.) Ethnic groups: African 99% (42 ethnic groups, most important being Fon, Adja, Yoruba, Bariba), Europeans 5,500 Religions: indigenous beliefs 50%, Christian 30%, Muslim 20% Languages: French (official), Fon and Yoruba (most common vernaculars in south), tribal languages (at least six major ones in north) Literacy: definition: age 15 and over can read and write; total population: 33.6%; male: 46.4%; female: 22.6% (2002 est.) |
|
| |
back to top |
|
Data code: BJ Government type: republicI ndependence: 1 August 1960 (from France) Legal system: based on French civil law and customary law; has not accepted compulsory ICJ jurisdiction Political pressure groups and leaders: NA |
|
| |
back to top |
|
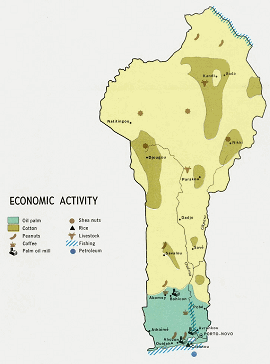
Economy - overview: The economy of Benin remains underdeveloped and dependent on subsistence agriculture, cotton production, and regional trade. Growth in real output has averaged around 5% in the past six years, but rapid population growth has offset much of this increase. Inflation has subsided over the past several years. In order to raise growth still further, Benin plans to attract more foreign investment, place more emphasis on tourism, facilitate the development of new food processing systems and agricultural products, and encourage new information and communication technology. Many of these proposals were included in Benin's $307 million Millennium Challenge Account grant signed in February 2006. The 2001 privatization policy continues in telecommunications, water, electricity, and agriculture in spite of government reluctance. The Paris Club and bilateral creditors have eased the external debt situation, with Benin benefiting from a G8 debt reduction announced in July 2005, while pressing for more rapid structural reforms. Benin continues to be hurt by Nigerian trade protection that bans imports of a growing list of products from Benin and elsewhere, which has resulted in increased smuggling and criminality in the border region. GDP - real growth rate: 4% (2006 est.) GDP - composition by sector: agriculture: 32.8%; industry: 13.7%; services: 53.5% (2006 est.) Labor force: 3.211 million (1996) Unemployment rate: NA% Population below poverty line: 33% (2001 est.) |
|
|
Agriculture - products: cotton, corn, cassava (tapioca), yams, beans, palm oil, peanuts; livestock Industries: textiles, food processing, construction materials, cement Industrial production growth rate: 8.3% (2001 est.) Exports: $563.1 million f.o.b. (2006 est.) Exports - commodities: cotton, crude oil, palm products, cocoa Exports - partners: China 31.3%, Indonesia 8.1%, India 7.4%, Niger 6%, Togo 4.8%, Thailand 4.8%, Nigeria 4.6% (2005) Imports: $927.3 million f.o.b. (2006 est.) Imports - commodities: foodstuffs, capital goods, petroleum products Imports - partners: France 21.8%, Ghana 7.1%, Cote d'Ivoire 7%, China 6.7%, UK 5.2%, Belgium 4.9%, Togo 4.5%, Thailand 4.2%, Nigeria 4% (2005) |
|
|
Currency (code): Communaute Financiere Africaine franc (XOF); note -
responsible authority is the Central Bank of the West African States
Exchange rates: Communaute Financiere Africaine francs (XOF) per US
dollar - 513.168 (2006), 527.47 (2005), 528.29 (2004), 581.2 (2003), 696.99
(2002) |
|
|
|
|
| |
back to top |
|
Telephone system: general assessment: NA; domestic: fair system of open-wire,
microwave radio relay, and cellular connections; Radio broadcast stations: AM 2, FM 9, shortwave 4 (2000) Television broadcast stations: 1 (2001) Internet country code: .bj Internet hosts: 867 (2006) Internet users: 425,000 (2005) |
|
| |
back to top |
|
Berzins R., Claro F., Akpona A.H. and Alfa Gambari Imorou S. 2007. Conservation du guépard et développement durable dans les aires protégées du nord Bénin. Mission d'enquête auprès des villageois et des agents d'aires protégées (16/12/2005-26/02/2006). Conservation of cheetahs in northern Benin. Zoological Society Paris, 57 pp. Claro F., Helder R. 2004. The cheetah in the Pendjari Reserve of Biosphere, Benin. Report of an identification mission (of march, 2004) Marker L., Malouf J. and Malouf A. 1999. Appendix 2: The status of the wild cheetah in its range countries. In: 1999 International Cheetah Studbook. http://www.cia.gov/cia/publications/factbook/geos/ao.html (update on 15 March, 2007) http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Benin http://www.lib.utexas.edu/maps/map_sites/country_sites.html#benin |