|
|
 |
| |
back to top | ||
|
Population. Still to be found in a few areas of south-east Algeria, between 3 1/2 E to the Libyan border and between 27 1/2 N to 20 1/2 N, with possible concentrations in Tassili N'Ajjer Range, Tassili Attoggar, and Tassili Teffedest. Females with two cubs are seen regularly by tribesman complaining that cheetah attack their camels. Rainfall was good from 1987-1990 in these areas, and there were increasing populations of Dorcas gazelle and Barbary sheep for cheetah to prey upon. It is thought that the majority of the remaining Algerian cheetahs are living in Tassili nr’Azger, because this plateau is far more rich in water and vegetation. It is difficult to see the last Algerian cheetahs. This country is a very important area for saving the North African cheetah. In 2005 a cheetah survey of the central zone of the Ahaggar National Park found fresh evidence of cheetahs (Wacher et al. 2005), but no estimate of the population size can be made on present data. Principal Threats. Restricted habitat, effects of drought on prey, and conflict with nomadic herders. |
|||
|
|
|||
|
| |||
|
|||
|
| |||
| Background: After more than a century of rule by France, Algerians fought through much of the 1950s to achieve independence in 1962. Algeria's primary political party, the National Liberation Front (FLN), has dominated politics ever since. Many Algerians in the subsequent generation were not satisfied, however, and moved to counter the FLN's centrality in Algerian politics. The surprising first round success of the Islamic Salvation Front (FIS) in the December 1991 balloting spurred the Algerian army to intervene and postpone the second round of elections to prevent what the secular elite feared would be an extremist-led government from assuming power. The army began a crack down on the FIS that spurred FIS supporters to begin attacking government targets. The government later allowed elections featuring pro-government and moderate religious-based parties, but did not appease the activists who progressively widened their attacks. The fighting escalated into an insurgency, which saw intense fighting between 1992-98 and which resulted in over 100,000 deaths - many attributed to indiscriminate massacres of villagers by extremists. The government gained the upper hand by the late-1990s and FIS's armed wing, the Islamic Salvation Army, disbanded in January 2000. However, small numbers of armed militants persist in confronting government forces and conducting ambushes and occasional attacks on villages. The army placed Abdelaziz BOUTEFLIKA in the presidency in 1999 in a fraudulent election but claimed neutrality in his 2004 landslide reelection victory. Longstanding problems continue to face BOUTEFLIKA in his second term, including the ethnic minority Berbers' ongoing autonomy campaign, large-scale unemployment, a shortage of housing, unreliable electrical and water supplies, government inefficiencies and corruption, and the continuing - although significantly degraded - activities of extremist militants. Algeria must also diversify its petroleum-based economy, which has yielded a large cash reserve but which has not been used to redress Algeria's many social and infrastructure problems. | |||
| |
back to top |
|
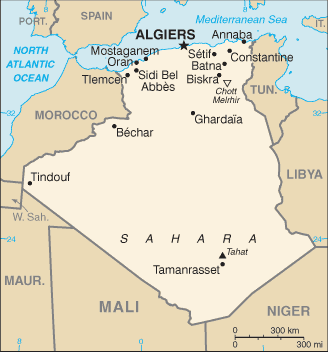
Area: total: 2,381,740 sq km; land: 2,381,740 sq km; water: 0 sq km Climate: arid to semiarid; mild, wet winters with hot, dry summers along coast; drier with cold winters and hot summers on high plateau; sirocco is a hot, dust/sand-laden wind especially common in summer Terrain: mostly high plateau and desert; some mountains; narrow, discontinuous coastal plain Natural resources: petroleum, natural gas, iron ore, phosphates, uranium, lead, zinc Land use: arable land: 3.17%; permanent crops: 0.28%; other: 96.55% (2005) Irrigated land: 5,690 sq km (2003) Natural hazards: mountainous areas subject to severe earthquakes; mudslides and floods in rainy season Environment - current issues: soil erosion from overgrazing and other poor farming practices; desertification; dumping of raw sewage, petroleum refining wastes, and other industrial effluents is leading to the pollution of rivers and coastal waters; Mediterranean Sea, in particular, becoming polluted from oil wastes, soil erosion, and fertilizer runoff; inadequate supplies of potable water. |
|
|
|
|
|
Environment - international agreements: party to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Environmental Modification, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Wetlands; signed, but not ratified: none of the selected agreements Geography - note: second-largest country in Africa (after Sudan) |
|
| |
back to top | |
|
Population: 32,930,091 (July 2006 est.) Age structure: 0-14
years: 28.1% (male 4,722,076/female 4,539,713); 15-64 years:
67.1% (male 11,133,802/female 10,964,502); Median
age: 0-14 years: 28.1% (male 4,722,076/female
4,539,713); 15-64 years: 67.1% (male 11,133,802/female 10,964,502); Population growth rate: 1.22% (2006 est.) Infant mortality rate: total: 29.87 deaths/1,000 live births; male: 33.62 deaths/1,000 live births; female: 25.94 deaths/1,000 live births (2006 est.) Life expectancy at birth: total population: 73.26 years; male: 71.68 years; female: 74.92 years (2006 est.) Total fertility rate: 1.89 children born/woman (2006 est.) HIV/AIDS - adult prevalence rate: 0.1% ; note - no country specific models provided (2001 est.) HIV/AIDS - people living with HIV/AIDS: 9,100 (2003 est.) HIV/AIDS - deaths: less than 500 (2003 est.) |
|
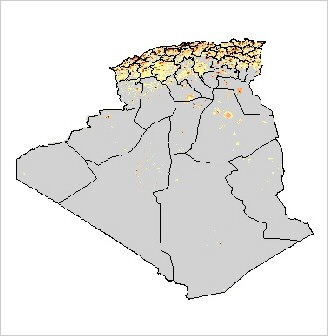
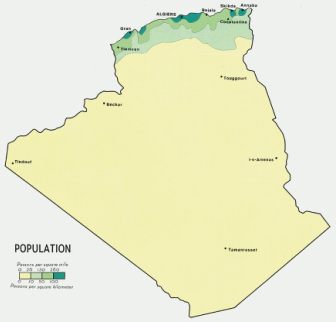
Distribution of the human population in Algeria |
|
Major infectious diseases: degree of risk: intermediate; food or waterborne diseases: bacterial diarrhea, hepatitis A, and typhoid fever; vectorborne disease: cutaneous leishmaniasis is a high risk in some locations (2005) |
||
|
Ethnic groups: Arab-Berber 99%, European less than 1%; note: almost all Algerians are Berber in origin, not Arab; the minority who identify themselves as Berber live mostly in the mountainous region of Kabylie east of Algiers; the Berbers are also Muslim but identify with their Berber rather than Arab cultural heritage; Berbers have long agitated, sometimes violently, for autonomy; the government is unlikely to grant autonomy but has offered to begin sponsoring teaching Berber language in schools Religions: Sunni Muslim (state religion) 99%, Christian and Jewish 1% Languages: Arabic (official), French, Berber dialects Literacy: definition: age 15 and over can read and
write; total population: 70%; male: 78.8%; female: 61%
(2003 est.) |
||
|
|
|
|
| back to top | |
|
Data Code: DZ Government type: republic Independence: 5 July 1962 (from France) Legal system: socialist, based on French and Islamic law; judicial review of legislative acts in ad hoc Constitutional Council composed of various public officials, including several Supreme Court justices; has not accepted compulsory ICJ jurisdiction Political pressure groups and leaders: The Algerian Human Rights League or LADH or LADDH [Yahia Ali ABDENOUR]; SOS Disparus [Nacera DUTOUR]; Somoud [Ali MERABET] |
|
| |
back to top |
|
|
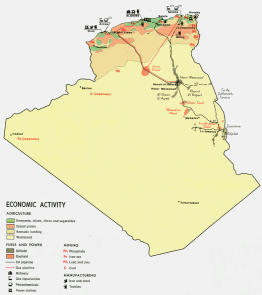
Economy - overview: The hydrocarbons sector is the backbone of the economy, accounting for roughly 60% of budget revenues, 30% of GDP, and over 95% of export earnings. Algeria has the seventh-largest reserves of natural gas in the world and is the second-largest gas exporter; it ranks 14th in oil reserves. Sustained high oil prices in recent years, along with macroeconomic policy reforms supported by the IMF, have helped improve Algeria's financial and macroeconomic indicators. Algeria is running substantial trade surpluses and building up record foreign exchange reserves. Algeria has decreased its external debt to less than 10% of GDP after repaying its Paris Club and London Club debt in 2006. Real GDP has risen due to higher oil output and increased government spending. The government's continued efforts to diversify the economy by attracting foreign and domestic investment outside the energy sector, however, has had little success in reducing high unemployment and improving living standards. Structural reform within the economy, such as development of the banking sector and the construction of infrastructure, moves ahead slowly hampered by corruption and bureaucratic resistance. |
|
GDP - real growth rate: 5.6% (2006 est.) GDP - composition by sector: agriculture: 9.4%; industry: 58.1%; services: 32.5% (2006 est.) Labor force: 9.31 million (2006 est.) Labor force - by occupation: agriculture 14%, industry 14%, construction and public works 10%, trade 13.4%, government 32%, other 10% (2003 est.) Unemployment rate: 15.7% (2006 est.) Population below poverty line: 25% (2005 est.) Agriculture - products: wheat, barley, oats, grapes, olives, citrus, fruits; sheep, cattle Industries: petroleum, natural gas, light industries, mining, electrical, petrochemical, food processing Industrial production growth rate: 10% (2006 est.) Exports: $55.6 billion f.o.b. (2006 est.) Exports - commodities: petroleum, natural gas, and petroleum products 97% Exports - partners: US 22.6%, Italy 16%, Spain 10.5%, France 10%, Canada 7.9%, Brazil 6.5%, Belgium 4.3%, Germany 4.2% (2005) Imports: $27.6 billion f.o.b. (2006 est.) Imports - commodities: capital goods, foodstuffs, consumer goods Imports - partners: France 28.1%, Italy 7.8%, Spain 7.2%, China 6.6%, Germany 6.3%, US 5.5% (2005) Currency (code): Algerian dinar (DZD) Exchange rates: Algerian dinars per US dollar - 73.2 (2006), 73.276 (2005), 72.061 (2004), 77.395 (2003), 79.682 (2002) |
|
| |
back to top |
|
Telephone system: general assessment: telephone density in Algeria is very low, not
exceeding five telephones per 100 persons; the number of fixed main lines
increased in the last few years to nearly 2.6 million, but only about
two-thirds of these have subscribers; much of the infrastructure is outdated
and inefficient Radio broadcast stations: AM 25, FM 1, shortwave 8 (1999) Television broadcast stations: 46 (plus 216 repeaters) (1995) Internet country code: .dz Internet hosts: 1,202 (2006) Internet users: 1.92 million (2005) |
|
| |
back to top |
|
Marker L., Malouf J. and Malouf A. 1999. Appendix 2: The status of the wild cheetah in its range countries. In: 1999 International Cheetah Studbook. Wacher T., de Smet K., Belbachir F., Belbachir-Bazi A., Fellous A., Belghoul M., Marker L. 2005. Sahelo–Saharan Interest Group Wildlife Surveys. Central Ahaggar Mountains (March 2005). http://www.lib.utexas.edu/maps/algeria.html |