|
|
 |
| back to top | |
|
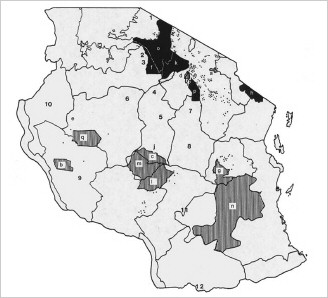
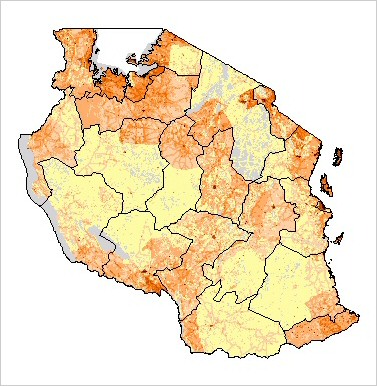
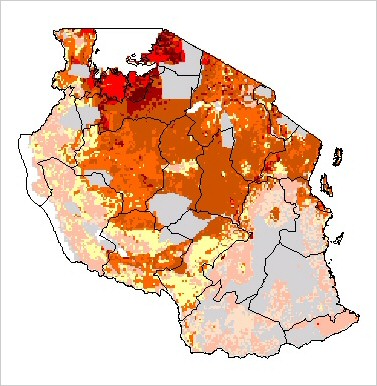
Population. Estimated at 1000, with a range of 500-1500. Found in the grasslands of Masailand and a few localized areas of woodlands. Populations do exist in the Serengeti/ Ngorongoro Conservation Area (25,000 km2), possibly as many as 500, however, the population suffers due to competition with lions and hyenas. There have been sightings in Mikumi National Park (3,230 km2), Tarangire National Park (2,600 km2), Katavi National Park (2,250 km2), and Ruaha National Park (10,200 km2). Gros (2002) estimated the population at 600-1000 individuals. Cheetahs are still widely distributed within the country, although range constriction appears to have started in central Tanzania. Established protected populations seem to be stable, although this could mask population decreases at a larger scale. Principal Threats. Poaching,
predation and competition with other large predators. |
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|||||||
| |
back to top | ||||||
|
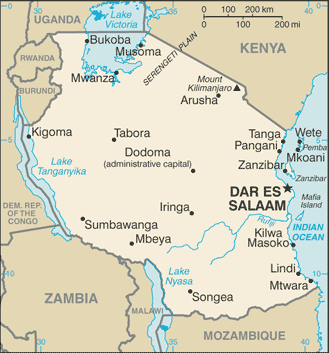
Area: total:
945,087 sq km; land: 886,037 sq km; water: 59,050 sq km Climate: varies from tropical along coast to temperate in highlands Terrain: plains along coast; central plateau; highlands in north, south Natural resources: hydropower, tin, phosphates, iron ore, coal, diamonds, gemstones, gold, natural gas, nickel Land use: arable land: 4.23%; permanent crops: 1.16%; other: 94.61% (2005) Irrigated land: 1,550 sq km (1998 est.) Natural hazards: flooding on the central plateau during the rainy season; drought Environment-current issues: soil
degradation; deforestation; desertification; destruction of coral reefs
threatens marine habitats; recent droughts affected marginal agriculture;
wildlife threatened by illegal hunting and trade, especially for ivory Environment-international agreements:
party to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto
Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the
Sea, Ozone Layer Protection, Wetlands Geography – note: Kilimanjaro is highest point in Africa; bordered by three of the largest lakes on the continent: Lake Victoria (the world's second-largest freshwater lake) in the north, Lake Tanganyika (the world's second deepest) in the west, and Lake Nyasa in the southwest |
|||||||
|
|
|
||||||
| |
back to top |
|
Population: 37,445,392 Age structure: 0-14 years: 43.7% (male 8,204,593/female 8,176,489); 15-64 years: 53.6% (male 9,906,446/female 10,178,066); 65 years and over: 2.6% (male 422,674/female 557,124) (2006 est.) Median age: total: 17.7 years; male: 17.5 years; female: 18 years (2006 est.) Population growth rate: 1.83% (2006 est.) Infant mortality rate: total: 96.48 deaths/1,000 live births; male: 105.64 deaths/1,000 live births; female: 87.05 deaths/1,000 live births (2006 est.) Life expectancy at birth: total population: 45.64 years; male: 44.93 years; female: 46.37 years (2006 est.) Total fertility rate: 4.97 children born/woman (2006 est.) |
|
|
HIV/AIDS - adult prevalence rate: 8.8% (2003 est.) HIV/AIDS - people living with HIV/AIDS: 1.6 million (2003 est.) HIV/AIDS - deaths: 160,000 (2003 est.) Major infectious diseases: degree of risk: very high; food or waterborne diseases: bacterial diarrhea, hepatitis A, and typhoid fever; vectorborne diseases: malaria, Rift Valley fever and plague are high risks in some locations; water contact disease: schistosomiasis (2005) Ethnic groups: mainland-native African 99% (of which 95% are Bantu consisting of more than 130 tribes), other 1% (consisting of Asian, European, and Arab); Zanzibar-Arab, native African, mixed Arab and native African Religions: mainland - Christian 30%, Muslim 35%, indigenous beliefs 35%; Zanzibar - more than 99% Muslim Languages: Kiswahili or Swahili (official), Kiunguju (name for Swahili in Zanzibar), English (official, primary language of commerce, administration, and higher education), Arabic (widely spoken in Zanzibar), many local languages note: Kiswahili (Swahili) is the mother tongue of the Bantu people living in Zanzibar and nearby coastal Tanzania; although Kiswahili is Bantu in structure and origin, its vocabulary draws on a variety of sources, including Arabic and English, and it has become the lingua franca of central and eastern Africa; the first language of most people is one of the local languages Literacy: definition: age 15 and over can read and write Kiswahili (Swahili), English, or Arabic; total population: 78.2%; male: 85.9%; female: 70.7% (2003 est.) |
|
| back to top | |
|
|
|
|
Data code: TZ Government type: republic Independence: 26 April 1964; Tanganyika became independent 9 December 1961 (from UK-administered UN trusteeship); Zanzibar became independent 19 December 1963 (from UK); Tanganyika united with Zanzibar 26 April 1964 to form the United Republic of Tanganyika and Zanzibar; renamed United Republic of Tanzania 29 October 1964 Legal system: based on English common law; judicial review of legislative acts limited to matters of interpretation; has not accepted compulsory ICJ jurisdiction Political pressure groups and leaders: NA |
|
| back to top | |
|
Economy-overview: Tanzania is one of the poorest countries in the world. The economy depends heavily on agriculture, which accounts for almost half of GDP, provides 85% of exports, and employs 80% of the work force. Topography and climatic conditions, however, limit cultivated crops to only 4% of the land area. Industry traditionally featured the processing of agricultural products and light consumer goods. The World Bank, the International Monetary Fund, and bilateral donors have provided funds to rehabilitate Tanzania's out-of-date economic infrastructure and to alleviate poverty. Long-term growth through 2005 featured a pickup in industrial production and a substantial increase in output of minerals, led by gold. Recent banking reforms have helped increase private-sector growth and investment. Continued donor assistance and solid macroeconomic policies supported real GDP growth of more than 6% in 2005. |
|
|
GDP - real growth rate: 6.8% (2005 est.) GDP - composition by sector: agriculture: 43.2%; industry: 17.2%; services: 39.6% (2004 est.) Labor force: 19.22 million (2005 est.) Labor force-by occupation: agriculture 80%, industry and services 20% (2002 est.) Population below poverty line: 36% (2002 est.) Agriculture-products: coffee, sisal, tea, cotton, pyrethrum (insecticide made from chrysanthemums), cashew nuts, tobacco, cloves, corn, wheat, cassava (tapioca), bananas, fruits, vegetables; cattle, sheep, goats Industries: agricultural processing (sugar, beer, cigarettes, sisal twine); diamond, gold, and iron mining, salt, soda ash; cement, oil refining, shoes, apparel, wood products, fertilizer Exports: $1.581 billion f.o.b. (2005 est.) Exports-commodities: coffee, manufactured goods, cotton, cashew nuts, minerals, tobacco, sisal (1996) Exports-partners: India 8.9%, Spain 8.2%, Netherlands 6.3%, Japan 5.7%, UK 4.9%, China 4.7%, Kenya 4.7% (2004) |
|
|
Imports: $2.391 billion f.o.b. (2005 est.) Imports-commodities: consumer goods, machinery and transportation equipment, industrial raw materials, crude oil Imports-partners: South Africa 12.7%, China 7.8%, India 6.4%, Kenya 5.4%, UAE 5.3%, US 4.8%, UK 4.6%, Zambia 4% (2004) Currency (code): Tanzanian shilling (TZS) Exchange rates: Tanzanian shillings per US dollar - 1,128.93 (2005), 1,089.33 (2004), 1,038.42 (2003), 966.58 (2002), 876.41 (2001) |
|
| |
back to top |
|
Telephone system: general assessment: fair system operating below capacity and being modernized for better
service; very small aperture terminal (VSAT) system under construction Radio broadcast stations: AM 12, FM 11, shortwave 2 (1998) Television broadcast stations: 3 (1999) Internet country code: .tz Internet hosts: 9,241 (2005) Internet users: 333,000 (2005) |
|
|
|
|
|
Gros P.M. 2002. The status and conservation of the cheetah Acinonyx jubatus in Tanzania. Biological Conservation 106, 177-185. Marker L., Malouf J. and Malouf A., 1999. Appendix 2: The status of the wild cheetah in its range countries. In: 1999 International Cheetah Studbook. http://www.cia.gov/cia/publications/factbook/geos/tz.html (last update on 29 March, 2006) |
|