|
|  |
| back to top | |
|
Population. Cheetah were reported as almost extinct from Malawi in 1996 and it appears that the species is now extirpated from this country mainly due to reduced habitat and prey as a result of an increased human population. Historically the cheetah was never widespread in this country due limited areas of suitable habitat and prey. Since 1980 cheetahs were only reported in three national parks along the western border with Zambia, the source of the cheetahs in Malawi. Given changes in Zambia as well as Malawi, it appears that there are no longer corridors for movement of cheetahs into Malawi, and the areas and prey base within the country cannot support viable populations (Purchase & Purchase 2007). Principal Threats. Human population growth, loss of habitat and poaching. | |
| back to top | |
| Established in 1891, the British protectorate of Nyasaland became the independent nation of Malawi in 1964. After three decades of one-party rule under President Hastings Kamuzu BANDA the country held multiparty elections in 1994, under a provisional constitution which came into full effect the following year. Current President Bingu wa MUTHARIKA, elected in May 2004 after a failed attempt by the previous president to amend the constitution to permit another term, struggled to assert his authority against his predecessor, culminating in MUTHARIKA quitting the political party on whose ticket he was elected into office. MUTHARIKA subsequently started his own party, the Democratic Progressive Party (DPP), and has continued with a halting anti-corruption campaign against abuses carried out under the previous regime. Increasing corruption, population growth, increasing pressure on agricultural lands, and the spread of HIV/AIDS pose major problems for the country. | |
| back to top | |
|
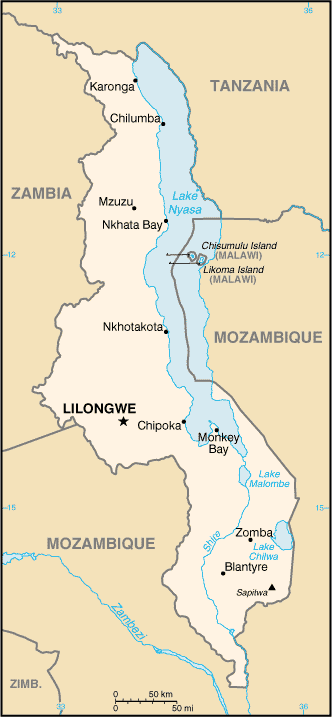
Area: total: 118,480 sq km; land: 94,080 sq km; water: 24,400 sq km Climate: tropical; rainy season (November to May); dry season (May to November) Terrain: narrow elongated plateau with rolling plains, rounded hills, some mountains Land use: arable land: 20.68%; permanent crops: 1.18%; other: 78.14% (2005) Natural resources: limestone, unexploited deposits of uranium, coal, and bauxite Environment-current issues: deforestation; land degradation; water pollution from agricultural runoff, sewage, industrial wastes; siltation of spawning grounds endangers fish populations Environment-international agreements: party to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Desertification, Endangered Species, Environmental Modification, Hazardous Wastes, Marine Life Conservation, Nuclear Test Ban, Ozone Layer Protection, Wetlands
signed, but not ratified: Law of the
Sea | |
|
|
|
| back to top | |
|
Population: 13,013,926 (July 2005 est.) Age structure: 0-14 years: 46.5% (male 3,056,522/female 3,000,493); 15-64 years: 50.8% (male 3,277,573/female 3,332,907); 65 years and over: 2.7% (male 139,953/female 206,478) (2006 est.) Median age: total: 16.5 years; male: 16.2 years; female: 16.8 years (2006 est.) Population growth rate: 2.38% (2006 est.) Infant mortality rate: total: 94.37 deaths/1,000 live births; male: 98.66 deaths/1,000 live births; female: 89.96 deaths/1,000 live births (2006 est.) Life expectancy at birth: total population: 41.7 years; male: 41.93 years; female: 41.45 years (2006 est.) Total fertility rate: 5.92 children born/woman (2006 est.) HIV/AIDS - adult prevalence rate: 14.2% (2003 est.) HIV/AIDS - people living with HIV/AIDS: 900,000 (2003 est.) HIV/AIDS - deaths: 84,000 (2003 est.) |
|
|
Ethnic groups: Chewa, Nyanja, Tumbuka, Yao, Lomwe, Sena, Tonga, Ngoni, Ngonde, Asian, European Languages: Chichewa 57.2% (official), Chinyanja 12.8%, Chiyao 10.1%, Chitumbuka 9.5%, Chisena 2.7%, Chilomwe 2.4%, Chitonga 1.7%, other 3.6% (1998 census) Religions: Christian 79.9%, Muslim 12.8%, other 3%, none 4.3% (1998 census) Literacy: definition: age 15 and over can read and writ; total population: 62.7%; male: 76.1%; female: 49.8% (2003 est.) |
|
| back to top | |
|
Data code: MI Government type: multiparty democracy Independence: 6 July 1964 (from UK) Legal system: based on English common law and customary law; judicial review of legislative acts in the Supreme Court of Appeal; accepts compulsory ICJ jurisdiction, with reservations | |
| back to top | |
|
Economy-overview: Landlocked Malawi ranks among the world's least developed countries. The economy is predominately agricultural, with about 85% of the population living in rural areas. Agriculture accounted for nearly 36% of GDP and 80% of export revenues in 2005. The performance of the tobacco sector is key to short-term growth as tobacco accounts for over 53% of exports. The economy depends on substantial inflows of economic assistance from the IMF, the World Bank, and individual donor nations. In 2006, Malawi was approved for relief under the Heavily Indebted Poor Countries (HIPC) program. The government faces many challenges, including developing a market economy, improving educational facilities, facing up to environmental problems, dealing with the rapidly growing problem of HIV/AIDS, and satisfying foreign donors that fiscal discipline is being tightened. In 2005, President MUTHARIKA championed an anticorruption campaign. Since 2005 President MUTHARIKA'S government has exhibited improved financial discipline under the guidance of Finance Minister Goodall GONDWE. GDP - real growth rate: 7% (2006 est.) GDP - composition by sector: agriculture: 35.4%; industry: 17.6%; services: 47% (2006 est.) Labor force: 4.5 million (2006 est.) Unemployment: NA Population below poverty: 53% (2004) Labor force-by occupation: agriculture 90%, industry and services 10% (2003 est.) Industries: tobacco, tea, sugar, sawmill products, cement, consumer goods Agriculture-products: tobacco, sugarcane, cotton, tea, corn, potatoes, cassava (tapioca), sorghum, pulses, groundnuts, Macadamia nuts; cattle, goats Exports: $513.1 million (f.o.b., 1995) Exports-commodities: tobacco 53%, tea, sugar, cotton, coffee, peanuts, wood products, apparel Exports-partners: US 17.8%, South Africa 11.2%, Egypt 7.6%, Germany 6.9%, Netherlands 6.8%, Japan 4.8%, Russia 4.6%, Mozambique 4.3%, UK 4.2% (2005) Imports: $767.9 million (f.o.b., 2006 est.) Imports-commodities: food, petroleum products, semimanufactures, consumer goods, transportation equipment Imports-partners: South Africa 36.3%, Zambia 9%, Zimbabwe 7.6%, Mozambique 7%, India 6.7%, Tanzania 4.8% (2005) Currency: 1 Malawian kwacha (MK) = 100 tambala Exchange rates: Malawian kwachas per US dollar - 135.96 (2006), 108.894 (2005), 108.898 (2004), 97.433 (2003), 76.687 (2002) | |
| back to top | |
|
Telephone system: domestic: system employs open-wire lines, microwave radio relay links, and radiotelephone communications stations; international: country code - 265; satellite earth stations - 2 Intelsat (1 Indian Ocean, 1 Atlantic Ocean) Radio broadcast stations: AM 9, FM 2 shortwave 2 (2001) Television broadcast stations: 1 (2001) Internet country code: .mw Internet hosts: 377 (2003) Internet users: 52,500 (2002) | |
| back to top | |
|
Marker L., Malouf J. and Malouf A. 1999. Appendix 2: The status of the wild cheetah in its range countries. In: 1999 International Cheetah Studbook. Purchase G. & Purchase D. 2007. Status of cheetah in Malai. Cat News Special Issue 3, 43. http://www.cia.gov/cia/publications/factbook/geos/mi.html (last update on 10 January, 2006) http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Malawi http://www.lib.utexas.edu/maps/map_sites/country_sites.html#malawi | |